Case study
Laser welding solutions for batteries connection through
nickel foils

SL – 80 PLUS
Picture 1

Picture 2
If high productivity is not required the most convenient option is to drive the laser (again source SL-80 Plus) through a focusing head controlled by a CNC machine. The following tests were conducted following the latter option.
The testing is realizing a circular weld over two nickel foils in two configurations:
A – Nickel foils thickness 0,2 mm + 0,1 mm (standard configuration)
B – Nickel foils thickness 0,1 mm + 0,1 mm (weight saving configuration).

Configutation A

Configutation B
Battery packs are now increasingly used in many sectors and applications. An effective and durable connection between the batteries is, of course, a key element. On this need, we carried out laser welding tests on nickel foils, which is an instance commonly encountered in battery packs.
Usually, on cells the thickness of the poles is more than 0,2 mm and we need to connect a 0,1 mm foil. Convenient way in these kinds of components is the overlapping laser welding. Given the thicknesses involved, the critical aspect of this operation is to join the sheets perfectly without sputtering at the backside. We can offer different options for solving this issue using laser welding, cause the laser beam can be driven
- manually
- by a CNC
- hrough a galvo
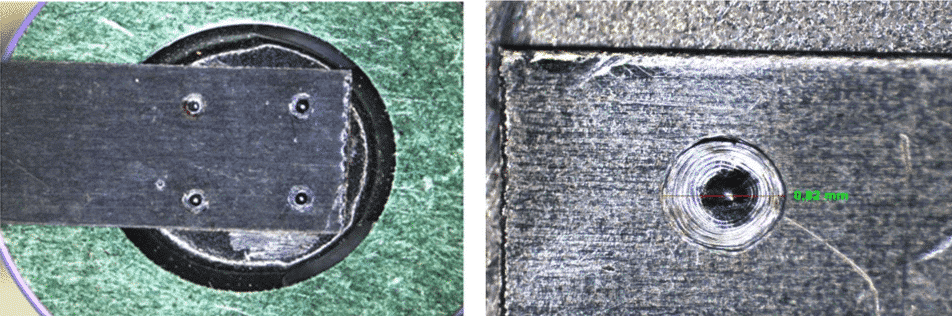
The sample in Picture 1, connection is made with a manual laser welding machine (SL-80 Plus).
The connection is made with 4 spots welds, each one measures approx 0,8 mm in diameter. This requires a precise tuning of parameters to avoid sputtering at the backside. It works, but it would be better if, instead of the 4 welding points, a small circle could be realised for a more secure bond. (Picture 2 ). So, in this case the best solution is a galvo welding machine due to the higher productivity (1 sec. per weld).
Picture 3
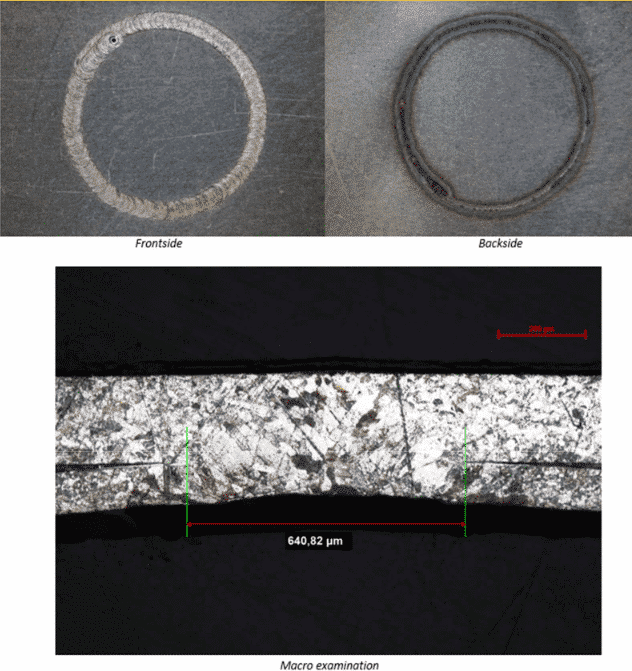
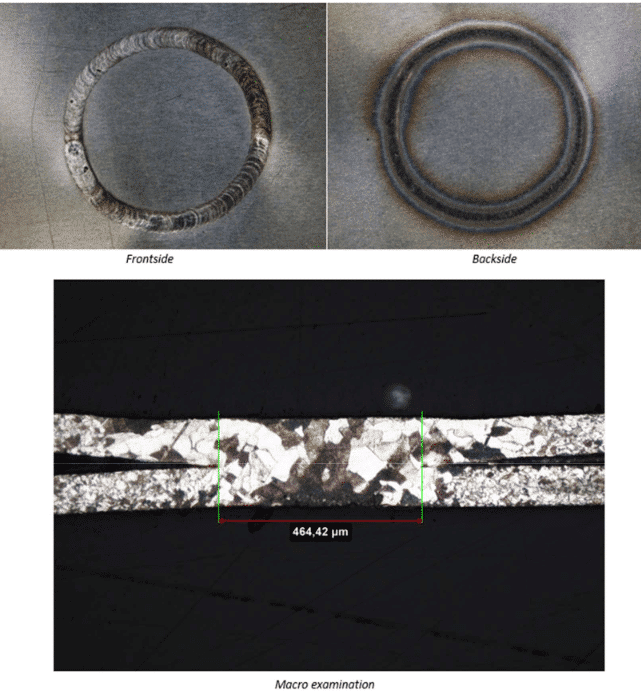
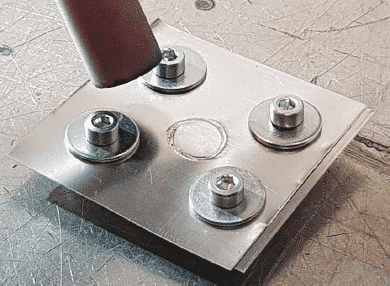
The goal is to obtain, in both configurations, full penetration without sputtering at the backside. To do this, the two foils must be perfectly connected. For the test, we simulate the job using nickel foils bolted together (Picture 3). Having obtained a good visual result for both configurations, an in-depth analysis was carried out, which yielded the following results:
Configutation A – Nickel foils thickness 0,2 mm + 0,1 mm (standard configuration)
Average power: 60 W
Shielding gas: Argon 5.0
Result is perfect: full penetration without defect. No metal sputtering at backside.
Configutation B – Nickel foils thickness 0,1 mm + 0,1 mm (weight saving configuration)
Average power: 50 W
Shielding gas: Argon 5.0
Result is perfect: full penetration without defect. No metal sputtering at backside.
Oops! We could not locate your form.
Curious about all Sisma applications for welding? Contact us, we will be happy to answer any questions you may have.


